This case note was developed in 2015 as part of the work for the 2nd edition of the Digital Preservation Handbook.
Business Continuity planning and practice involves organizations proactively preparing for potential incidents and disruptions in order to avoid suspension of critical operations and services, or if operations and services are disrupted, that they resume operations and services as rapidly as required by those who depend on them. The development and use of a business continuity plan based on sound principles, endorsed by senior management, and activated by trained staff will greatly reduce the likelihood and severity of impact of disasters and incidents. It is an important component of ensuring bit preservation and makes a significant contribution to digital preservation through this.
The Data Archive is the UK national data centre for the Social Sciences funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC). The Archive holds certification to ISO 27001, the international standard for information security, which requires information security continuity to be embedded in an organisation's business continuity management systems. The digital storage system at the Data Archive is based, for security purposes, on segregated and distributed storage and access. Business continuity at the Data Archive is based around the resilience provided by creating multiple copies of the data and specified recovery procedures, alongside pre-emptive failure prevention. Each file from any dataset has at minimum three copies. The Archive also creates a read only archival copy of each study and any update as it is made available on the system.
The Data Archive is the UK national data centre for the Social Sciences funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC). The Data Archive has over 7000 mainstream digital datasets or studies, comprising over 1.35 million individual files occupying 2.1TB storage. The Archive holds certification to ISO 27001, the international standard for information security, which requires information security continuity to be embedded in an organisation's business continuity management systems (ISO/IEC 27001:2013, A.17.1).
The digital storage system at the Data Archive is based, for security purposes, on segregated and distributed storage and access.
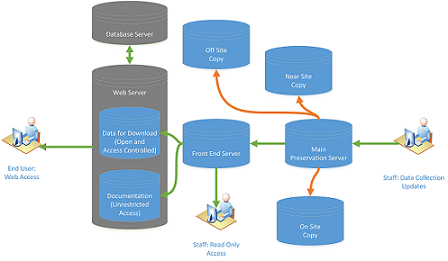
Business continuity at the Data Archive is based around the resilience provided by creating multiple copies of the data and specified recovery procedures, alongside pre-emptive failure prevention. Each file from any dataset has at minimum three copies. The Archive also creates a read only archival copy of each study and any update as it is made available on the system (these exist for the period since 2008, prior to 2008 changes were embedded as part of the study). :
Main copy: This is the master copy which holds all preservation data on the master preservation server.
Shadow copy: At least one shadow copy is made. As files are updated, they are "shadowed" onto a separate server in the main system.
Off-site near-line copy: An off-site, near-line copy is kept in case of a major disaster at Essex. Studies are kept as encrypted and versioned bundles.
Disasters can occur in different forms and at varying levels. The Data Archive aims to identify issues through validation procedures, including checksums. Preventative measures are also in place, using RAID 6 and RAID 10, to flag media failures and allow replacement before data loss. In addition it has in place a range of recovery measures designed to meet any conceivable disaster.
Corrupt file supplied
A file is supplied with corrupt information that is not detected through Data Processing
Solution
The file is re-requested from the supplier as there would be no earlier version within the Archive's system.
Corrupt file identified in existing holdings
A file is found with corrupt information
Solution
- The file is restored from the shadow area.
- A read only version of the file (created at the time of ingest/update) is retrieved to replace the corrupted version.
Unreadable file
A single file is unreadable from the media
Solution
- The medium is checked to make certain that this is an isolated problem. If it is found to affect the complete medium the disaster recovery procedure is activated.
- If the poblem is isolated then the problematic file is recreated from the shadow copy.
Corrupt media
In this case a complete medium is damaged or cannot be reliably read.
Solution
- The use of preventative technology to identify the possibility of a medium failing or being wholly corrupted makes this highly unlikely, but a copy would be created on a new medium from an uncorrupted version.
Corrupt shadow area as well as main area
In this situation both the main and shadow areas cannot be read, nor any of the additional copies.
Solution
- This is very unlikely due to the number of checks that are made but in the event, the study or data would be re-created from the versions bundled copy from either near site or from the off-site copy.
Complete loss of data at the University of Essex
In this scenario, all of the data held at the University of Essex are unreadable and all of the systems are damaged beyond repair. (Major disaster.)
Solution
- The main systems would be rebuilt and data would be retrieved from the off-site copy.
Segregation and multi-resilience
Image: Data Archive University of Essex CC BY 3.0
(Click on image above to see a larger version)
This case note was developed in 2015 as part of the work for the 2nd edition of the Digital Preservation Handbook (Digital Preservation Coalition, 2015). For further information see Risk and change management.
References
Digital Preservation Coalition, 2015. Digital Preservation Handbook. Available: http://www.dpconline.org/advice/preservationhandbook
ISO, 2013. ISO/IEC 27001:2013. Information technology -- Security techniques -- Information security management systems -- Requirements. Available: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail?csnumber=54534